模仿实现Linux下 \(readelf\) 工具部分功能
完整实现:
https://github.com/JiaZhengJingXianSheng/ReadELF
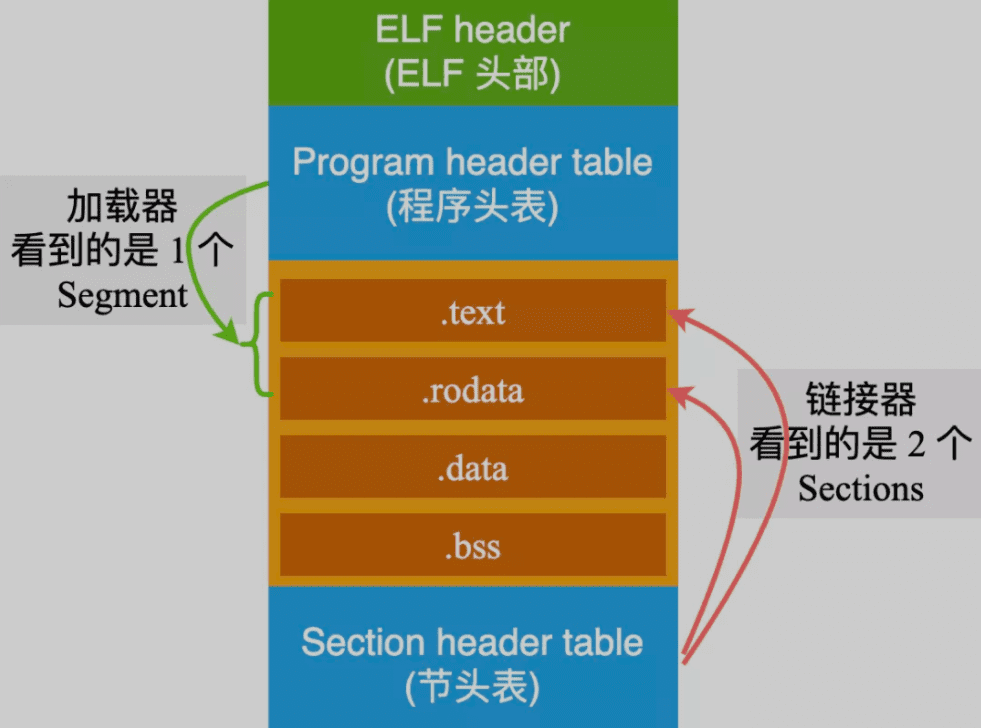
ELF 目标文件格式的最前部是 ELF文件头 (ELF
Header) ,它包含了描述整个文件的基本属性,比如 ELF
文件版本、目标机器型号、程序入口地址等。紧接是 ELF 文件各个段。其中ELF
文件中与段有关的重要结构就是 段表 (Section Header
Table) ,该表描述了ELF
文件包含的所有段的信息,比如每个段的段名、段的长度、在文件中的偏移、读写权限及段的其他属性。

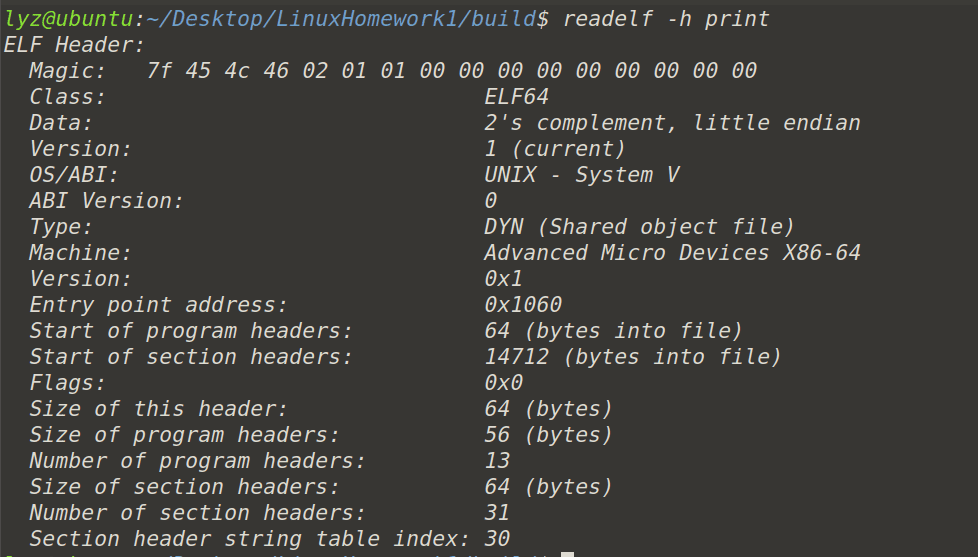
在 linux 下elf的定义存放在 \(/usr/include\) 下, 我们可以用 \(readelf -h\)
命令加上文件来查看ELF头文件。

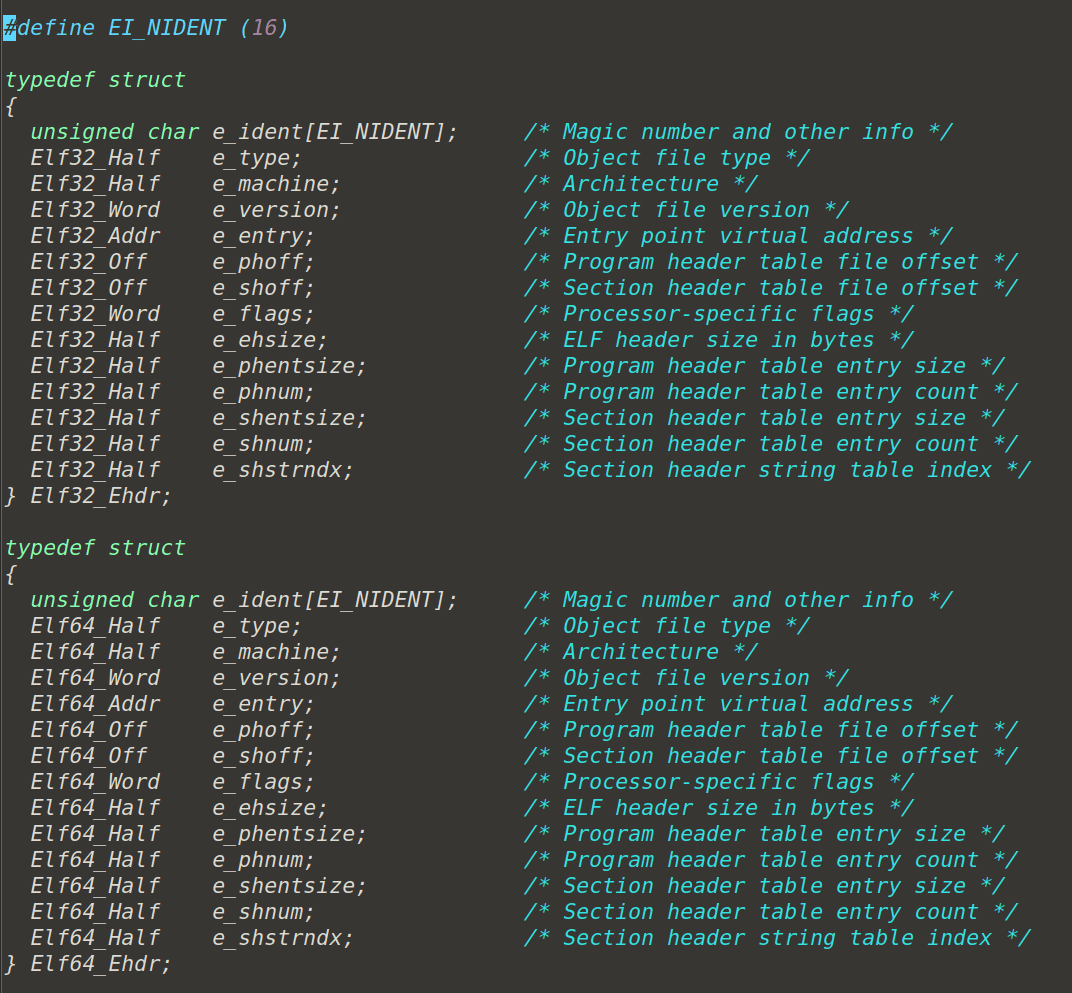
ELF 的文件头中定义了 ELF
魔数、文件机器字节长度、数据存储方式、版本、运行平台、ABI版本、ELF
重定位类型、硬件平台、硬件平台版本,入口地址、程序头入口和长度、段表的位置和长度及段的数量等。
详细请参照:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ZOvHG_ofiU6iWtoSR9bFow
头文件 -h功能

我们拿 ELF 文件头结构跟前面readelf输出的 ELF
文件头信息相比照,可以看到输出的信息与 ELF
文件头中的结构很多都一一对应。有点例外的是 “Elf64_ Ehdr”
中的e_ident这个成员对应了readelf
输出结果中的“Class”、Data”、“Version”、“OS/ABI”和“ABI
Version”这5个参数。剩下的参数与“EIf64_ Ehdr”中的成员都一一对应。
细节请参照:https://www.cnblogs.com/jiqingwu/p/elf_explore_2.html
所以我们在c语言实现时,只需要按照结构体定义依次取值,并判断输出。下面提供简单部分代码,完整代码会附在文章开头。其中reinterpret_cast运算符是用来处理无关类型之间的转换;它会产生一个新的值,这个值会有与原始参数(expression)有完全相同的比特位。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| const Elf64_Ehdr *header;
header = reinterpret_cast<Elf64_Ehdr *>(programMMap);
printf("Magic:\t\t\t\t\t");
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i)
{
printf("%02x ", header->e_ident[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("类型:\t\t\t\t\t");
switch (header->e_ident[4])
{
case 0:
printf("无效\n");
break;
case 1:
printf("ELF32\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("Elf64\n");
break;
default:
printf("错误\n");
break;
}
printf("数据存储方式:\t\t\t\t");
switch (header->e_ident[5])
{
case 0:
printf("未知格式\n");
break;
case 1:
printf("二进制补码 小端存储\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("二进制补码 大端存储\n");
break;
default:
printf("错误\n");
break;
}
printf("版本:\t\t\t\t\t");
printf("%d\n", (int)header->e_ident[8]);
|
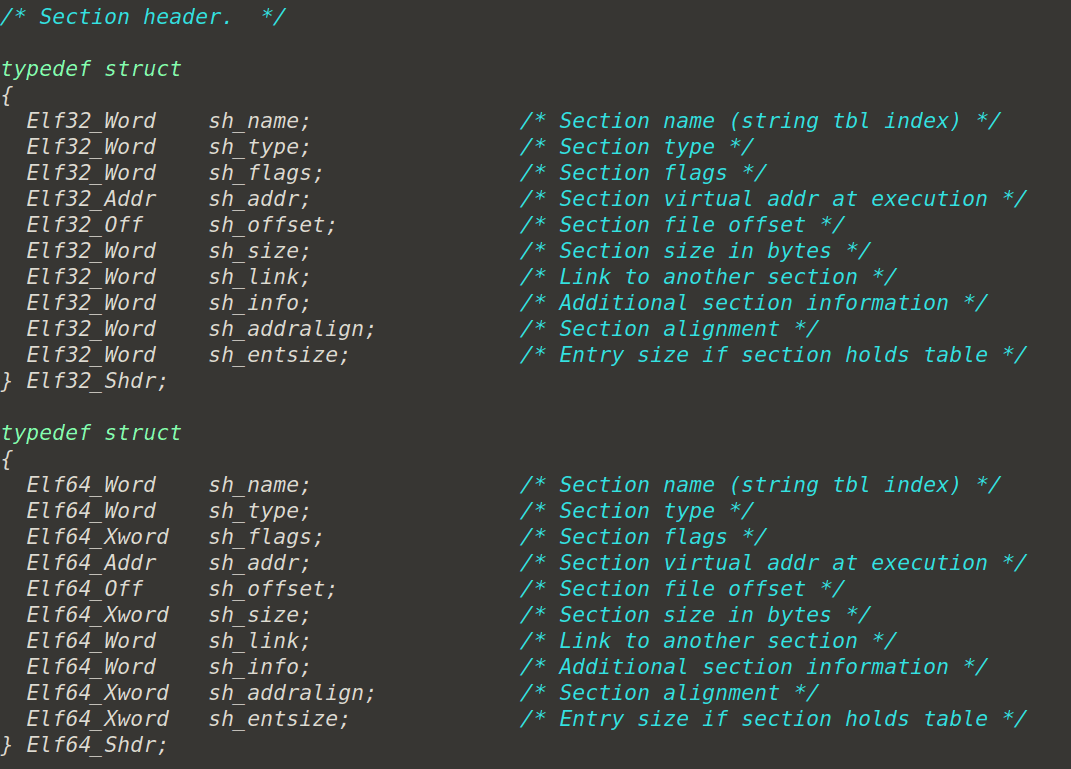
段表 -S功能

ELF 文件中有很多各种各样的段,这个段表 (Section Header
Table)就是保存这些段的基本属性的结构。段表是 ELF
文件中除了文件头以外最重要的结构,它描述了ELF
的各个段的信息,比如每个段的段名、段的长度、在文件中的偏移、读写权限及段的其他属性。也就是说,ELF
文件的段结构就是由段表决定的,编译器、链接器和装载器都是依靠段表来定位和访问各个段的属性的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| lyz@ubuntu:~/Desktop/LinuxHomework1/build$ readelf -S print
There are 31 section headers, starting at offset 0x3978:
Section Headers:
[Nr] Name Type Address Offset
Size EntSize Flags Link Info Align
[ 0] NULL 0000000000000000 00000000
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 0
[ 1] .interp PROGBITS 0000000000000318 00000318
000000000000001c 0000000000000000 A 0 0 1
[ 2] .note.gnu.propert NOTE 0000000000000338 00000338
0000000000000020 0000000000000000 A 0 0 8
[ 3] .note.gnu.build-i NOTE 0000000000000358 00000358
0000000000000024 0000000000000000 A 0 0 4
[ 4] .note.ABI-tag NOTE 000000000000037c 0000037c
0000000000000020 0000000000000000 A 0 0 4
[ 5] .gnu.hash GNU_HASH 00000000000003a0 000003a0
0000000000000024 0000000000000000 A 6 0 8
[ 6] .dynsym DYNSYM 00000000000003c8 000003c8
00000000000000a8 0000000000000018 A 7 1 8
[ 7] .dynstr STRTAB 0000000000000470 00000470
00000000000000b7 0000000000000000 A 0 0 1
[ 8] .gnu.version VERSYM 0000000000000528 00000528
000000000000000e 0000000000000002 A 6 0 2
[ 9] .gnu.version_r VERNEED 0000000000000538 00000538
0000000000000020 0000000000000000 A 7 1 8
[10] .rela.dyn RELA 0000000000000558 00000558
00000000000000c0 0000000000000018 A 6 0 8
[11] .rela.plt RELA 0000000000000618 00000618
0000000000000018 0000000000000018 AI 6 24 8
[12] .init PROGBITS 0000000000001000 00001000
000000000000001b 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 4
[13] .plt PROGBITS 0000000000001020 00001020
0000000000000020 0000000000000010 AX 0 0 16
[14] .plt.got PROGBITS 0000000000001040 00001040
0000000000000010 0000000000000010 AX 0 0 16
[15] .plt.sec PROGBITS 0000000000001050 00001050
0000000000000010 0000000000000010 AX 0 0 16
[16] .text PROGBITS 0000000000001060 00001060
0000000000000185 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 16
[17] .fini PROGBITS 00000000000011e8 000011e8
000000000000000d 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 4
[18] .rodata PROGBITS 0000000000002000 00002000
0000000000000004 0000000000000004 AM 0 0 4
[19] .eh_frame_hdr PROGBITS 0000000000002004 00002004
0000000000000044 0000000000000000 A 0 0 4
[20] .eh_frame PROGBITS 0000000000002048 00002048
0000000000000108 0000000000000000 A 0 0 8
[21] .init_array INIT_ARRAY 0000000000003d98 00002d98
0000000000000008 0000000000000008 WA 0 0 8
[22] .fini_array FINI_ARRAY 0000000000003da0 00002da0
0000000000000008 0000000000000008 WA 0 0 8
[23] .dynamic DYNAMIC 0000000000003da8 00002da8
0000000000000210 0000000000000010 WA 7 0 8
[24] .got PROGBITS 0000000000003fb8 00002fb8
0000000000000048 0000000000000008 WA 0 0 8
[25] .data PROGBITS 0000000000004000 00003000
0000000000000010 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 8
[26] .bss NOBITS 0000000000004010 00003010
0000000000000008 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 1
[27] .comment PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00003010
000000000000002a 0000000000000001 MS 0 0 1
[28] .symtab SYMTAB 0000000000000000 00003040
0000000000000618 0000000000000018 29 46 8
[29] .strtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 00003658
0000000000000203 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[30] .shstrtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 0000385b
000000000000011a 0000000000000000 0 0 1
Key to Flags:
W (write), A (alloc), X (execute), M (merge), S (strings), I (info),
L (link order), O (extra OS processing required), G (group), T (TLS),
C (compressed), x (unknown), o (OS specific), E (exclude),
l (large), p (processor specific)
|
我们通过起始地址加上e_shoff来指向我们的段表,并根据具体细节判断输出。
1
| sTable = reinterpret_cast<Elf64_Shdr *>(programMMap + header->e_shoff);
|
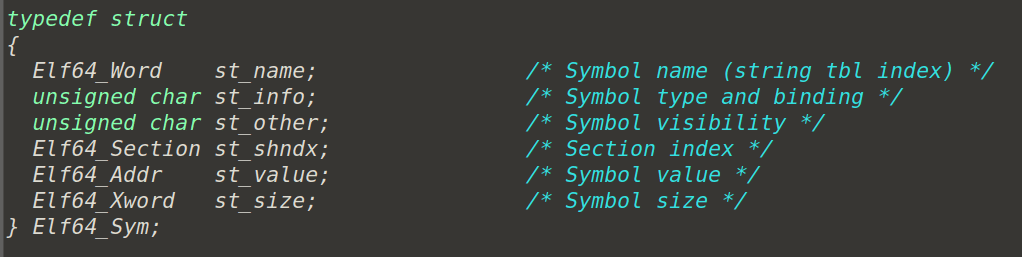
-s 功能
ELF符号表定义如下
接下来我们用段表的段偏移当作索引去找拿出他的symbol_table,并判断是否为
\(.dynamic和.symtab\)
根据具体对应值输出即可。
详细对应关系在 \(/usr/include/elf.h\) 宏定义的备注。

细节可参考:https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-255670.htm
参考链接:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ZOvHG_ofiU6iWtoSR9bFow
https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-255670.htm
https://github.com/cyyzero/readelf
https://www.cnblogs.com/jiqingwu/p/elf_explore_2.html
参考书目:
《程序员的自我修养》 俞甲子、石凡、潘爱民著